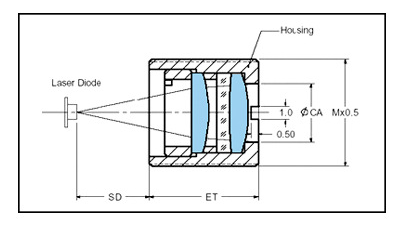
Shell Material: Copper, Aluminum (Blackened Treatment)
Lens material:D-LAK6、L-BAL35、H-K9L、D-ZK3、LBAL42
Size:M6、M7、M8、M9、M10 (can be customized according to requirements)
Type: Single piece, two-piece, three piece, single rubber ring, double rubber ring
Wavelength:450nm、520nm、530nm、633nm、635nm、650nm、655nm、780nm、850nm、400-700nm
Coating:400-700nm、630-680nm、400-700nm、700-1100nm、420-680nm、786nm、510nm-550nm、420-660nm、405-450nm
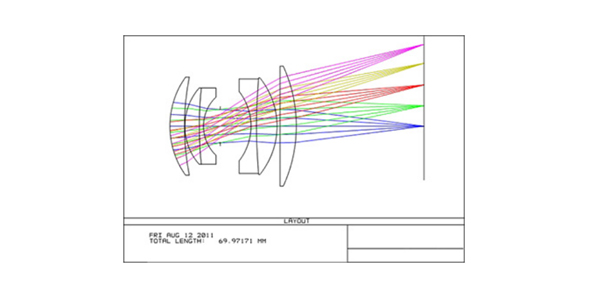
Non spherical collimating lens group
A collimating lens refers to an instrument that can transform the light rays from each point in the aperture column into a parallel collimated beam of light.
The lens type depends on the aberration requirements. For those with low requirements, simple monolithic lenses such as plano convex or biconvex lenses can be used, and larger relative apertures are allowed. For those with high requirements, double laminated lenses are used, and the relative aperture is appropriately reduced. In grating systems, especially when the grating is thick and the gap is small, aberration has little effect on the formation of Moir é fringes. Therefore, a single planar convex lens can be used with the plane facing the filament to reduce aberration. In the case of large gaps, reducing aberrations, especially chromatic aberration, can improve stripe contrast. In this case, it is advisable to use a dual plate plano convex lens with the first plane facing the filament, or use an aberration correcting double laminated lens. It must be pointed out that compared to the divergence angle of the filament, the aberration of the lens is secondary.
The focal length of a lens is related to the maximum allowable relative aperture. For a single plate plano convex lens, the relative aperture should not be greater than 0.8, for a single plate biconvex lens, it should not be greater than 0.5, and for a double plate plano convex lens, it should not be greater than 1. When used with large gaps, the above values should be appropriately reduced. Usually, within the allowable range, shorter focal lengths are used in most cases. This not only makes the size of the reading head more compact, but also greatly improves the illumination on the silicon photovoltaic cell, thereby reducing the heat generated by the lighting power and making the system more stable. However, choosing a short focal length will increase lens aberration and filament divergence angle, and make the illumination within the light transmission range more uneven, which is a disadvantageous aspect.