A lens is an optical component made of transparent materials such as glass, crystal, etc. A lens is a refractive mirror, whose refractive surface is a transparent body consisting of two spherical surfaces (part of the spherical surface) or one spherical surface (part of the spherical surface) and one plane. It forms both real and virtual images. Lenses can generally be divided into two categories: convex lenses and concave lenses. A lens with a central portion thicker than the edge portion is called a convex lens, which has three types: biconvex, plano convex, and concave convex; A concave lens with a thinner central part than the edge part is called a concave lens, which can be divided into three types: double concave, flat concave, and convex concave.
Classification of lenses:
Convex lenses have the function of converging light rays, so they are also called converging lenses; Positive lens (can be used for farsightedness and reading glasses). This type of lens can be divided into:
a. Double concave lens; It is a two-sided lens;
b. Flat concave lens; It is a lens with one concave side and one flat side;
c. Convex concave lens; A lens with one convex side and one concave side.
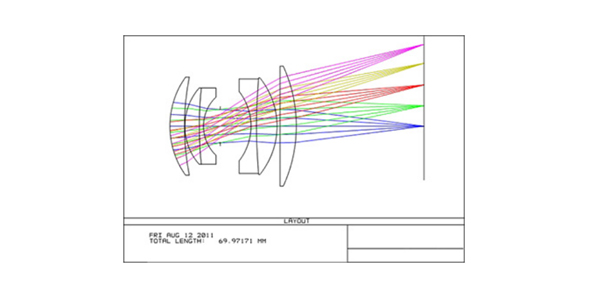
Thin lens - a lens whose thickness in the central part is relatively large compared to the curvature radius on both sides. In the early days, cameras were only equipped with a convex lens lens, hence they were called single lenses. With the continuous development of technology, modern lenses have several different forms and functions of convex concave lenses forming a converging lens, called a compound lens. The concave lens in a compound lens serves to correct various aberrations.
Optical glass has high transparency, purity, colorlessness, uniform texture, and good refractive ability, making it the main raw material for lens production. Due to differences in chemical composition and refractive index, optical glasses include:
1. flint glass - adding lead oxide to the glass composition to increase the refractive index (1.8804);
2. Crown glass - made by adding sodium oxide and calcium oxide to the glass composition to reduce its refractive index (the refractive index of barium crown glass is 1.7055);
3. Lanthanide crown glass - a variety discovered in recent years, it has excellent characteristics of high refractive index and low dispersion, providing conditions for creating large aperture advanced lenses.

Lens imaging principle
A glass or plastic component used in lighting fixtures that can change the direction of light or control the distribution of light.
The lens is the most basic optical component that makes up the optical system of a microscope. The objective lens, eyepiece, and condenser lens are all composed of single or multiple lenses. According to their different shapes, they can be divided into two categories: convex lenses (positive lenses) and concave lenses (negative lenses).
When a beam of light parallel to the main optical axis passes through a convex lens and intersects at a point, this point is called the focal point, and the plane passing through the focal point and perpendicular to the optical axis is called the focal plane. There are two focal points. The focal point in the object space is called the object focal point, and the focal plane at that point is called the object focal plane; On the contrary, at the focal point of the image square space, called the image square focal point, the focal plane at that point, called the image square focal plane, forms an upright virtual image after passing through a concave lens, while a convex lens forms an inverted real image. Real images can be displayed on the screen, while virtual images cannot.
Imaging law of convex lens:
Object distance (u) Image distance (v) Inverted, size, virtual real application
u>2f F
u=2f v=2f Inverted, equal size, real image, characteristics: size boundary point
f
u=f v=∞ Non imaging, characteristics: boundary point between virtual and real
uv Upright magnification, virtual image, magnifying glass